Electric vehicle adoption is rapidly increasing, surpassing expert predictions as governments worldwide introduce incentives, automakers expand EV offerings, and public and private sectors invest heavily in charging infrastructure. This surge is further fueled by a growing environmental consciousness, pushing consumers towards greener transportation options and reducing harmful emissions. As EVs become more commonplace, understanding the different Ev Charger Levels is crucial for every EV owner and prospective buyer. Knowing the nuances of each level ensures you can select the most suitable electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) for your needs, whether at home, work, or on the road.
Decoding Level 1 EV Charging: The Slow and Steady Option
Level 1 EV charging stands as the most basic and consequently the slowest among ev charger levels. It operates on a standard 120-volt AC household outlet in North America, delivering power in the range of 1 kilowatt (kW) to 1.8 kW. This system utilizes a common 3-prong household plug on one end and a J1772 (Type 1) connector on the other, which interfaces with the electric vehicle. It’s worth noting that Level 1 charging is not a viable option in Europe, where standard residential electricity operates at 230 volts.
Level 1 Charging Speed and Practicality
As the most leisurely of the ev charger levels, Level 1 can require a significant time investment, typically ranging from 22 to 40 hours to fully replenish a standard battery electric vehicle (BEV) from an empty state. In terms of range gained per hour of charging, you can expect to add approximately 3 to 7 miles (4 to 11 kilometers). Despite its slow pace, Level 1 charging compatibility is universal; it’s suitable for all Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs). Notably, Level 1 chargers are often included as standard equipment when purchasing an EV.
The primary use case for Level 1 ev charger levels is home charging, often employed as a supplementary or “trickle” charge solution. It also serves as a convenient backup when faster Level 2 or Level 3 charging stations are inaccessible. However, due to its protracted charging times, Level 1 is generally not practical for public charging scenarios unless time is not a constraint, such as overnight parking.
| EV Charging Level | Connector Type | Typical Output Power | Estimated Charge Time (40kWh Battery) | Estimated Range Per Hour of Charging | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | J1772 (Type 1) | 1 kW – 1.8 kW | 22 – 40 hours | 3 – 7 miles (4 – 11 kilometers) | Home charging, Backup charging |


Alt text: Level 1 EV charger connector with a standard household plug and J1772 vehicle connector, illustrating basic electric vehicle supply equipment.
Level 2 EV Charging: Balancing Speed and Convenience
Level 2 EV charging represents a significant upgrade in speed compared to Level 1 within the spectrum of ev charger levels. In North America, it utilizes a 208-volt to 240-volt AC outlet, while in Europe, it operates on 230-volt (single-phase) or 400-volt (three-phase) outlets. Power output for Level 2 chargers in North America can reach up to 19.2 kW (80A), and in Europe, up to 22 kW. Level 2 chargers often incorporate advanced functionalities such as RFID card authentication, load balancing to manage power distribution, and OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) networking for integration into charging networks.
Connector types for Level 2 charging vary geographically. North America and Japan use the J1772 (Type 1) connector, whereas Europe utilizes the Mennekes (Type 2) connector. Level 2 charging stations are available in both tethered (cable permanently attached) and untethered (socket-only, requiring a separate cable) configurations. Currently, Level 2 ev charger levels are the most prevalent type of EV charging infrastructure globally, although Level 3 charger deployments are experiencing rapid growth.
Level 2 Charging Speed and Deployment Scenarios
Level 2 chargers deliver a substantially faster charging experience, potentially up to 19 times quicker than Level 1, contingent on the charger’s power output and the vehicle’s charge acceptance rate. An hour of charging at Level 2 can add between 10 to 75 miles (16 to 120 kilometers) of driving range.
Level 2 ev charger levels are the most common choice for public charging stations and are also widely adopted for home and workplace installations. They are frequently found in locations such as hotels, retail centers, and grocery stores, making them ideally suited for overnight charging at home or during work hours.
| EV Charging Level | Connector Type | Typical Output Power | Estimated Charge Time (40kWh Battery) | Estimated Range Per Hour of Charging | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 2 | J1772 (North America), Mennekes (Europe) | 3 kW – 22 kW | 2 – 13 hours | 10 – 75 miles (16 – 120 kilometers) | Workplace charging, Hotel charging, Overnight charging, Public charging |
Alt text: Level 2 EV charging connectors, showcasing the J1772 and Mennekes plugs commonly used for medium-speed electric vehicle charging.
Both Level 1 and Level 2 ev charger levels are categorized as AC-type EV chargers. To fully grasp the distinctions of Level 3 charging, it’s important to understand the fundamental difference between AC and DC EV charging.
AC vs. DC EV Charging: Understanding the Core Difference
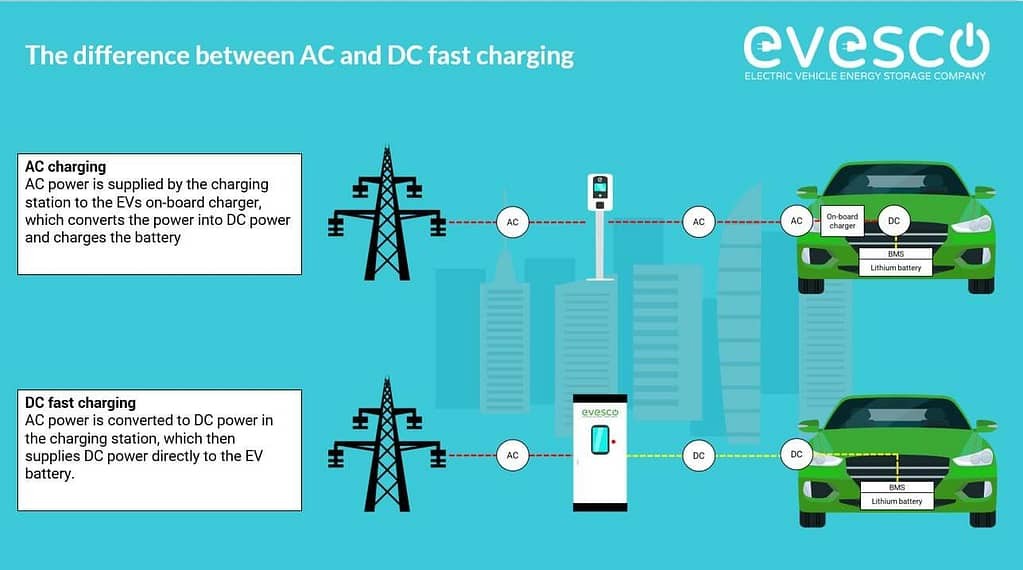
Electric vehicle charging fundamentally relies on two types of electrical current: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). The electrical grid distributes power as AC, while EV batteries store energy as DC. The critical distinction between AC and DC ev charger levels lies in where the AC-to-DC power conversion occurs.
With AC charging (Level 1 and Level 2), the conversion from AC to DC happens within the electric vehicle itself, using an onboard charger. This process can be relatively slow due to the limitations of the vehicle’s onboard charger. Conversely, DC charging (Level 3) performs the AC-to-DC conversion within the charging station before delivering power to the vehicle. This bypasses the onboard charger’s limitations, enabling a much higher power delivery and, consequently, faster charging speeds. This fundamental difference is what makes DC ev charger levels significantly faster than AC charging options.
Alt text: Diagram illustrating how DC fast charging works, showing the AC to DC conversion within the charging station and direct power flow to the EV battery.
Level 3 EV Charging: Unleashing DC Fast Charging Power
Level 3 EV charging, often referred to as DC fast charging, represents the pinnacle of speed among ev charger levels. These charging stations are the quickest and most powerful options available in the EV charging landscape. Level 3 chargers utilize a three-phase power supply, typically 480-volt in North America and 400-volt in Europe, and can deliver power outputs exceeding 360 kW.
Level 3 charging stations often come equipped with advanced features such as dynamic power distribution, allowing for efficient allocation of power across multiple vehicles, multi-charging protocol cables to support various EV standards, and network connectivity via OCPP for seamless integration with charging networks. Level 3 chargers are available in both stationary configurations for permanent installations and portable versions for mobile charging solutions.
Connector types for Level 3 ev charger levels include CCS (Combined Charging System) connectors (CCS 1 in North America, CCS 2 in Europe), CHAdeMO, and Tesla Superchargers (NACS). While “Level 3” is broadly used for all kW ratings of DC fast charging, technically, its origins refer to charging power levels above 400 kW.
Level 3 Charging Speed and Strategic Deployment
As previously mentioned, Level 3 chargers perform AC-to-DC conversion internally, allowing for direct and rapid power delivery to the EV battery. This results in significantly faster charging times. A Level 3 charger can potentially fully charge a standard electric car in under 20 minutes, depending on the vehicle’s battery capacity and charge acceptance rate.
Level 3 ev charger levels are strategically deployed in locations where rapid charging is essential, such as public service stations along highways, making them indispensable for long-distance travel. Their importance is also growing in other sectors, including EV fleet charging and auto dealerships, as well as any location where vehicles require quick turnarounds, like delivery and logistics hubs.
| EV Charging Level | Connector Type | Typical Output Power | Estimated Charge Time | Estimated Range Per Hour of Charging | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 3 | CCS 1 (North America), CCS 2 (Europe), CHAdeMO (Japan), Tesla (NACS) | 30 kW – 360 kW+ | 15 mins – 1.5 hours* (depending on charge acceptance rate) | 120 – 1400+ miles (193 – 2250+ kilometers) | Highway services, Fleet charging, Car dealerships, Logistics hubs, Distribution centers |
Alt text: Illustration explaining DC fast charging, highlighting its speed and suitability for quick battery replenishment at public charging stations.
Choosing the Right EV Charger Level for Your Needs
Understanding the nuances of ev charger levels is vital for making informed decisions about EV charging solutions. Level 1 charging offers basic convenience, primarily for home use. Level 2 provides a significant speed increase and is suitable for home, workplace, and public charging. Level 3 DC fast charging delivers the quickest charging experience for long journeys and commercial applications. Selecting the appropriate charging level depends on your individual driving habits, charging location options, and time constraints. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure efficient and convenient charging for your electric vehicle.