Buying a new car is an exciting experience, but amidst the thrill of choosing features and models, understanding car insurance is crucial. For the most part, insuring a new car isn’t drastically different from insuring any other vehicle. The type and amount of coverage you’ll need primarily depend on factors like your location and any specific requirements from your lender if you’re financing your new vehicle with a car loan.
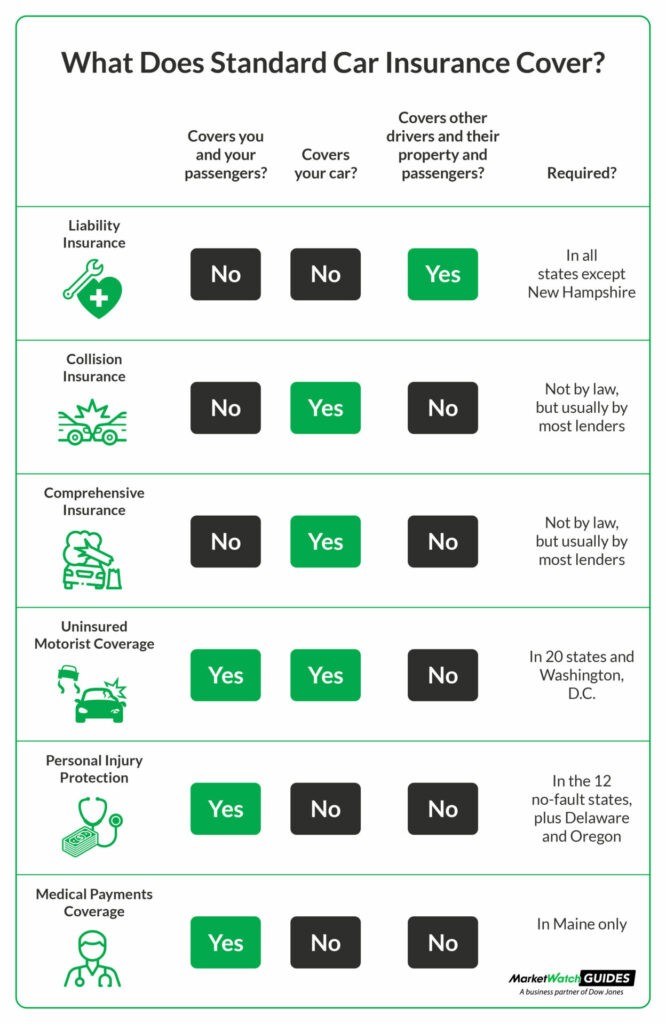 Chart detailing six standard car insurance coverages and what they cover
Chart detailing six standard car insurance coverages and what they cover
State Minimum Car Insurance Requirements for New Vehicles
Every state sets its own minimum car insurance requirements. These regulations, typically established by the state’s Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or a similar agency, can vary significantly from state to state. These minimums are the least amount of coverage you can legally carry.
State minimum requirements usually consist of variations of the standard auto insurance coverage types. To determine the specific car insurance mandates in your state and explore cost-effective provider options, you can often find resources online by searching for “[your state] minimum car insurance requirements.”
Standard Types of Car Insurance Coverage Required for New Cars
State minimum car insurance requirements for new cars almost always include some combination of the following standard coverage options:
- Liability Coverage: This is typically the cornerstone of any car insurance policy. It consists of two parts:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Covers costs if you injure someone else in an accident you cause. This can include their medical bills, lost wages, and legal fees.
- Property Damage Liability: Covers damages to another person’s property if you are at fault in an accident. This usually means damage to their vehicle, but can also include fences or buildings.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Protects you if you’re hit by a driver who either has no insurance or doesn’t have enough insurance to cover your damages. This coverage can help pay for your medical bills and car repairs in these situations.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): In some states, PIP coverage is required and helps pay for your medical expenses and lost wages after an accident, regardless of who was at fault.
Lender Requirements for New Car Insurance
If you’re taking out a loan to purchase your new car, your lender will likely have specific car insurance requirements beyond your state’s minimums. These additional requirements are in place to protect the lender’s financial interest in the vehicle. Since the car is collateral for the loan, lenders want to ensure it’s protected against damage.
Lenders commonly require these extra car insurance coverages:
- Collision Coverage: This coverage pays for damage to your new car if you collide with another vehicle or object, regardless of who is at fault. It essentially covers accidents where your car is damaged from impact.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This protects your new car against almost any other type of damage besides collisions. This includes events like theft, vandalism, fire, hail, animal damage, and natural disasters.
These lender-mandated coverages ensure that if your new car is damaged or stolen, there will be funds available to repair or replace it, safeguarding the lender’s investment.
Additional Car Insurance Options for New Cars
Beyond the standard and lender-required coverages, many insurance companies offer a range of optional add-on coverages that can be particularly beneficial for new car owners. These options provide extra layers of protection and convenience.
Here are some common and helpful optional car insurance coverages for new cars:
- Roadside Assistance: This coverage is incredibly useful, especially with a new car where you might expect fewer mechanical issues but still want peace of mind. Roadside assistance covers services like towing, jump-starts, fuel delivery if you run out of gas, and flat tire changes.
- Rental Reimbursement: If your new car is damaged in a covered accident and needs to be in the shop for repairs, rental reimbursement coverage helps pay for the cost of a rental car so you’re not stranded without transportation.
- Mechanical Breakdown Insurance (MBI): Think of this as similar to an extended warranty, but from your car insurance company. MBI covers repairs to certain mechanical components of your new car after a breakdown, protecting you from unexpected repair bills as your car ages.
- Gap Insurance: If your new car is totaled or stolen, gap insurance covers the “gap” between what your car is worth (its actual cash value) and what you still owe on your car loan. New cars depreciate quickly, so this can be very valuable to avoid being underwater on your loan.
- New Car Replacement Coverage: This option is often available for brand new vehicles. If your new car is totaled within a certain period (e.g., the first year or two), this coverage will pay to replace it with a brand new car of the same make and model, rather than just the depreciated value.
Exploring these additional car insurance options when buying a new car allows you to tailor your policy to your specific needs and risk tolerance, providing enhanced protection and peace of mind as you enjoy your new vehicle. Talking to an insurance agent can help you understand all available options and choose the best coverage for your situation.